UART
Note
The following example uses the Raspberry Pi-compatible 40PIN pins and Qualcomm universal 40PIN pins of Rhino Pi-X1. For their specific location distinction, refer to Hardware Information.
UART Overview UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a microchip with programmable functionality, used to control the interface between a computer and its connected serial devices.
Preparation
- One Rhino Pi-X1 device
- One CH340 test board
- Three Dupont wires
- One Windows computer with a
serial port debugging toolinstalled
Connection
- Connect the USB port of the CH340 to a USB interface on the Windows computer.
- Connect the TTL interface of the CH340 to the Raspberry Pi-compatible interface of Rhino Pi-X1 as follows:
| Rhino Pi-X1 | <---> | CH340 |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_16 (RX) | <---> | TX |
| PIN_29 (TX) | <---> | RX |
| PIN_14 (GND) | <---> | GND |

Testing
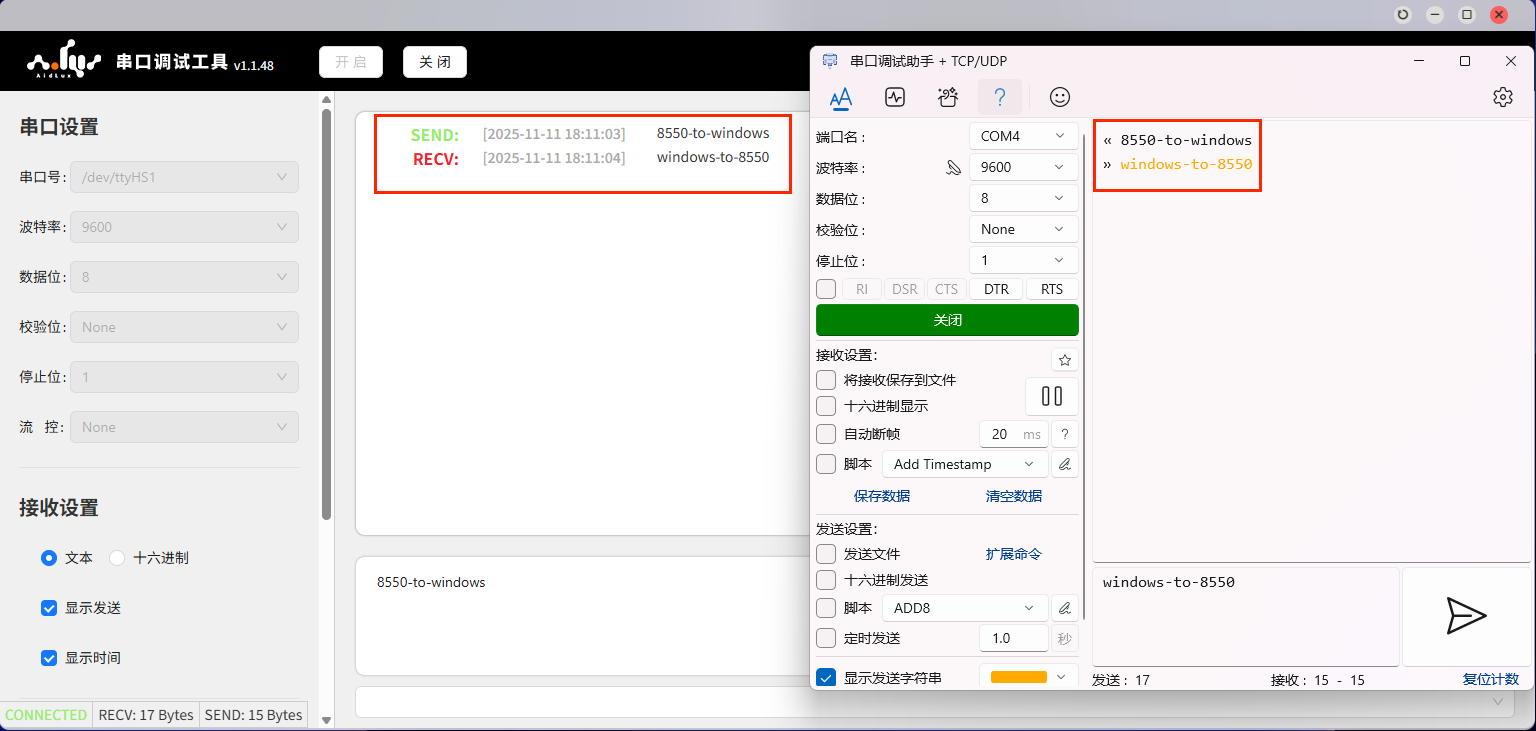
- Open the serial port debugging tool on the Windows computer, select the connected port, set the baud rate to 9600, and open the port.
- Go to the App Center on the Rhino Pi-X1 Web desktop, download the UartCheck tool. After opening the tool, select the serial port number: /dev/ttyHS1, set the baud rate to 9600, and enable the serial port.
Note
To download the UartCheck tool, log in to the Rhino Pi-X1 Web desktop, click the App Center button at the bottom, and search for and download it. For the Web login method, refer to Web Login.
- Send messages to each other and verify that both sides can receive the messages.
Expansion
Rhino Pi-X1 is equipped with multiple groups of UART interfaces. The corresponding relationship between specific PIN numbers and device numbers is shown in the table below:
| PIN Number | <---> | Device Number |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_16 (RX) & PIN_29 (TX) (Raspberry Pi 40PIN side) | <---> | /dev/ttyHS1 |
| PIN_11 (RX) & PIN_13 (TX) (Universal 40PIN side) | <---> | /dev/ttyHS3 |