AidLux System Usage FAQs
Q1: QtScrcpy screen capture software previously connected and displayed the screen normally, but now only shows a white screen after connection and fails to display the device interface – what could be the cause?
A: This issue is usually caused by QtScrcpy program exceptions or cache mechanism errors, a known software-level defect.
Recommended solutions: Close and restart QtScrcpy to check if the problem persists; if the exception continues, uninstall the current version and reinstall the latest version of QtScrcpy.
Q2: The AidLux hybrid system is already installed – how to switch to the LE system?
A: First, ensure that all flashing-related tools (USB driver, ADB, flashing tool, etc.) are installed correctly. Then follow the flashing steps in the official documentation to replace the system with the LE version. Reference Link
Q3: The AidLux Web remote port 8000 is accessible, but Terminal, filebrowser, and aidcode are not – what is the issue?
A: Since the remote desktop terminal is inaccessible, we need to log in directly to AidLux Linux and execute the following command to check the nginx status:
ps -ef|grep nginx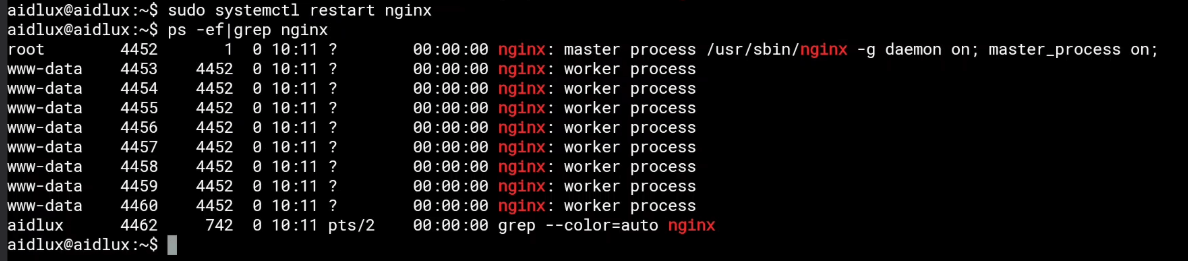
Try starting nginx manually:
# Enterprise Edition
sudo systemctl restart nginx
# Applicable to all versions (default password: aidlux)
sudo nginxAfter nginx starts, the nginx process should display as follows:

Under normal circumstances, remote web access to Terminal, filebrowser, and aidcode should now work properly.
Q4: How to set custom services/scripts to start automatically on boot?
A: Refer to Autostart Service Configuration
Q5: How to disable rild on Rhino Pi X1?
A:
- Log into the Android shell using
adb shell - Elevate privileges to the root user with
su - Finally, run
setprop ctl.stop vendor.ril-daemonto disable rild
Q6: What scenarios require flashing firmware on Rhino Pi X1?
A:
- Changing the system type (e.g., flashing from Linux to Android)
- Upgrading/iterating the Linux system firmware
- Accidentally flashing firmware from other manufacturers
Note
Note: The flashing methods for corresponding scenarios are as follows:
a. For flashing scenarios 1 and 2, refer to System Burning
b. How to recover if the firmware is mistakenly flashed with that of other manufacturers
Q7: Why does a forbid 403 error appear when uploading files?
A: This error usually occurs due to permission issues. The file drag-and-drop upload function uses the aidlux user by default. If the target upload folder is not created by the aidlux user, or if the user does not have read/write permissions for the directory, a 403 error will occur.
Solutions:
Create the target folder using the aidlux user; or run the command:
sudo chmod -R 777 <folder path>Or grant read/write permissions to the aidlux user:
sudo chown aidlux:aidlux <folder path>Q8: The development board’s IP address is 192.168.1.x – why can’t VNC be used for remote connection?
A: This issue is usually caused by network address conflicts. The development board is preconfigured or manually set to use a fixed IP in the 192.168.1.x network segment, while the DHCP address pool of the connected hotspot or router is also assigned in the same segment (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24), resulting in conflicts.
Solutions: Set the development board to obtain an IP automatically (DHCP mode); or manually modify the development board’s IP to a non-conflicting segment (e.g., 192.168.10.x); also ensure the computer and development board are on the same local area network.
Q9: The system only recognizes the WAN port (eth0), and eth1 and other interfaces are not displayed in ip a
A: The wired network design of Rhino Pi X1 is similar to a router structure. By default, only the power-side network port is configured as the WAN port (for external network connection), and the other three are LAN ports for providing local area network connections to other devices. When a cable is plugged into a LAN port, the system automatically switches to an internal network segment (usually 192.168.1.x), so it is normal for only eth0 to be displayed at the system level.
Explanation: The WAN port is for external network access; LAN ports are for internal device networking;
The board supports modifying the LAN network segment, which can be adjusted as needed.
Q10: How to remotely debug Python programs in AidLux?
A: Enable Ubuntu Desktop for VNC remote debugging, or use ssh aidlux@<IP> to directly enter the container and execute debugging commands, or use VSCode SSH Remote to access and write code remotely.
Extended Supplementary Explanations (Optional Reference)
QtScrcpy White Screen Troubleshooting Extension:
- If restarting/reinstalling does not resolve the issue, check if the device’s screen resolution exceeds QtScrcpy’s supported range (lower the device resolution and try again);
- Verify if the USB connection mode is set to "Charging only" (switch to "File transfer" or "USB debugging" mode);
- Clear QtScrcpy’s cache directory (usually
~/.config/QtScrcpyon Windows/macOS,~/.local/share/QtScrcpyon Linux).
nginx Startup Failure Handling:
- If
sudo nginxreports a port occupation error, runsudo lsof -i :80to check the occupied port and kill the conflicting process; - Check nginx configuration file errors with
sudo nginx -t(common issues: incorrect path configuration, syntax errors in/etc/nginx/conf.d/); - For enterprise edition, if
systemctl restart nginxfails, check the service status withsudo systemctl status nginxfor detailed error logs.
- If
Boot Autostart Service Advanced Configuration:
- For Python scripts, create a
.servicefile in/etc/systemd/system/(example):ini[Unit] Description=Custom Python Script After=network.target [Service] User=aidlux ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 /home/aidlux/script.py Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target - Enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable custom-script.service && sudo systemctl start custom-script.service.
- For Python scripts, create a
403 File Upload Error Advanced Fix:
- Avoid using
777permissions (security risk); assign minimal permissions:sudo chmod 755 <folder>+sudo chown aidlux:aidlux <folder>; - For Filebrowser upload failures, check the Filebrowser configuration file (usually
/etc/filebrowser.json) to confirm the root directory’s owner isaidlux.
- Avoid using
LAN Segment Modification for Rhino Pi X1:
- Modify the LAN segment configuration file:
sudo vi /etc/dnsmasq.conf(adjustaddress=/lan/192.168.10.1to the target segment); - Restart the network service:
sudo systemctl restart network-manager.
- Modify the LAN segment configuration file: