AidConnect Developer Documentation
Overview
AidLux is a hybrid system integrating Android and Linux, equipped with capabilities such as streaming media processing and AI inference acceleration. With the iterative development of the product, some customers hope to use AidLux as a service carrier to leverage its processing capabilities for data interaction with third-party (customer-owned) applications. To meet this demand, AidConnect was developed.
AidConnect is built on AidIPC and supports high-speed data transmission of custom sizes between AidLux and third-party applications. Developers can add the name and size of communication channels either through SDK interfaces or manual configuration. After configuration, the communication channels can be accessed in Android or Linux environments for data reading and writing.
Taking a third-party application calling AidLux's AI inference capability as an example, the complete process is as follows:
- Add the communication channel name and size in the AidLux App via the interface or SDK;
- If configured manually, restart the AidLux App for the settings to take effect; channels added via the SDK take effect immediately;
- The Android application writes source data through the configured channel;
- The AidLux Linux side reads the data from the corresponding channel and performs AI inference;
- After inference is completed, write the result data to another channel;
- The Android application reads the inference result from this channel and executes subsequent logic.
With AidConnect, AidLux enables efficient and flexible data flow and AI capability sharing between Android and Linux, as well as with third-party applications.
Development Process
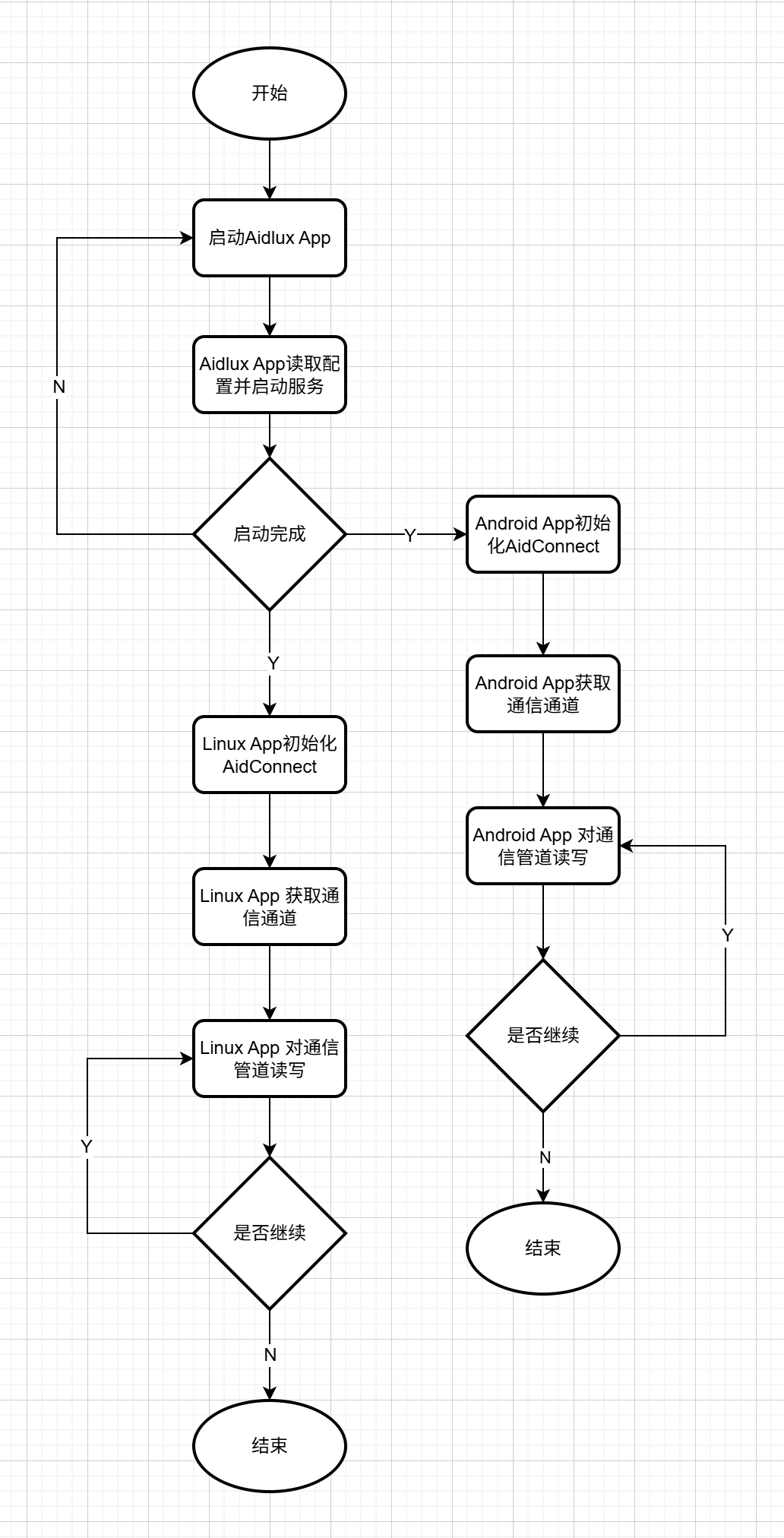
Support Status
| Linux | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| C++ | ✅ | / |
| Python | 🚧 | / |
| Kotlin/Java | / | ✅ |
✅: Supported 🚧: Planned to be supported
Quick Start
Installation
sudo aid-pkg update
## Ubuntu 20.04
sudo aid-pkg -i -d aidconnect_1.0.0.2_arm64_ub2004.aid.gpg
## Ubuntu 22.04
sudo aid-pkg -i -d aidconnect_1.0.0.2_arm64_ub2204.aid.gpg Contact AidLux to obtain the AidConnect Android SDK and integrate it into your Android projectGetting Started with Examples
The following examples demonstrate how AidConnect enables data transmission between Linux and Android. The transmission requires pre-defining the transmission channel either through manual configuration or via the AidConnect Android SDK interface (choose one of the two methods). The transmission channel configuration is stored in the AidLux App at /etc/opt/aidlux/memory_config.
If configuring the transmission channel manually, follow these rules:
- Open the
memory_configfile and manually add a JSON object under thecustomer_block_arraynode. The JSON object contains the name and size (in megabytes) of the transmission channel. For example:
# Defines a "test" channel with a size of 1MB
{"cap":6,"m":3,"n":5,"size":5,"block":5,"customer_block_array":[{"name":"test","size":1}]}Note
The following points should be noted when developing with the AidConnect SDK for C++:
- After installing the AidConnect C++ SDK, the header file is stored at:
/usr/local/include/aidlux/aidconnect/aidconnect.hpp - After installing the AidConnect C++ SDK, the dynamic library is stored at:
/usr/local/lib/aidlux/aidconnect/libaidconnect.so - After installing the AidConnect C++ SDK, sample programs are stored at:
/usr/local/share/aidconnect/examples
// AidConnect initialization
Aidlux::AidConnect aidconnect;
int status = aidconnect.init();
if(EXIT_SUCCESS != status){
printf("aidconnect.init failed !\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Get the channel
status = aidconnect.aidconnect_with_name("test");
if(EXIT_SUCCESS != status){
printf("aidconnect.aidkv_with_id failed !\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Write data to the channel
char aaa[] = "Hello Cpp";
printf("Set string[%s], length[%d]\n", aaa, (int)sizeof(aaa));
status = aidconnect.set_bytes(aaa, sizeof(aaa));
if(EXIT_SUCCESS != status){
printf("aidconnect.set_bytes failed !\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Read data from the channel
char* result = new char[10000];
uint64_t length = 0;
status = aidconnect.get_bytes(&result, &length);
if(EXIT_SUCCESS != status){
printf("aidconnect.get_bytes failed !\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
printf("Result string[%s], length[%ld]\n", result, length);// AidConnect initialization
AidConnect.initialize(application, true, new AidConnectCallback() {
@Override
public void initCallback(boolean isInitSuccess, Set<String> keys) {
if (isInitSuccess) {
} else {
}
}
});
// Add a channel named "test" with a size of 1MB
Set<String> channels = AidConnect.addChannelWithName("test", 1);
if (channels == null) {
Log.e("Activity", "addChannelWithName failed");
}
// Remove the channel
Set<String> channels = AidConnect.removeChannelWithName("test");
if (channels == null) {
Log.e("Activity", "removeChannelWithName failed");
}
// Get the channel
AidConnect aidConn = AidConnect.aidConnectWithName("test");
if (aidConn == null) {
Log.e("Activity", "aidConnectWithName failed");
} else {
}
// Write data to the channel
byte[] buffer = new byte[3840*2160*3];
boolean setFlag = aidConn.setBytes(buffer);
if (setFlag == true) {
Log.i("Activity", "setBytes successfully");
} else {
Log.e("Activity", "setBytes failed");
}
// Read data from the channel
byte[] buffer = new byte[3840*2160*3];
byte[] bytes = aidConn.getBytes(buffer, 3840*2160*3);
if (bytes == null) {
Log.e("Activity", "getBytes failed");
} else {
}
// Release AidConnect resources
int ret = AidConnect.release();
if (ret == 0) {
Log.i("Activity", "release successfully");
} else {
Log.e("Activity", "release failed");
}